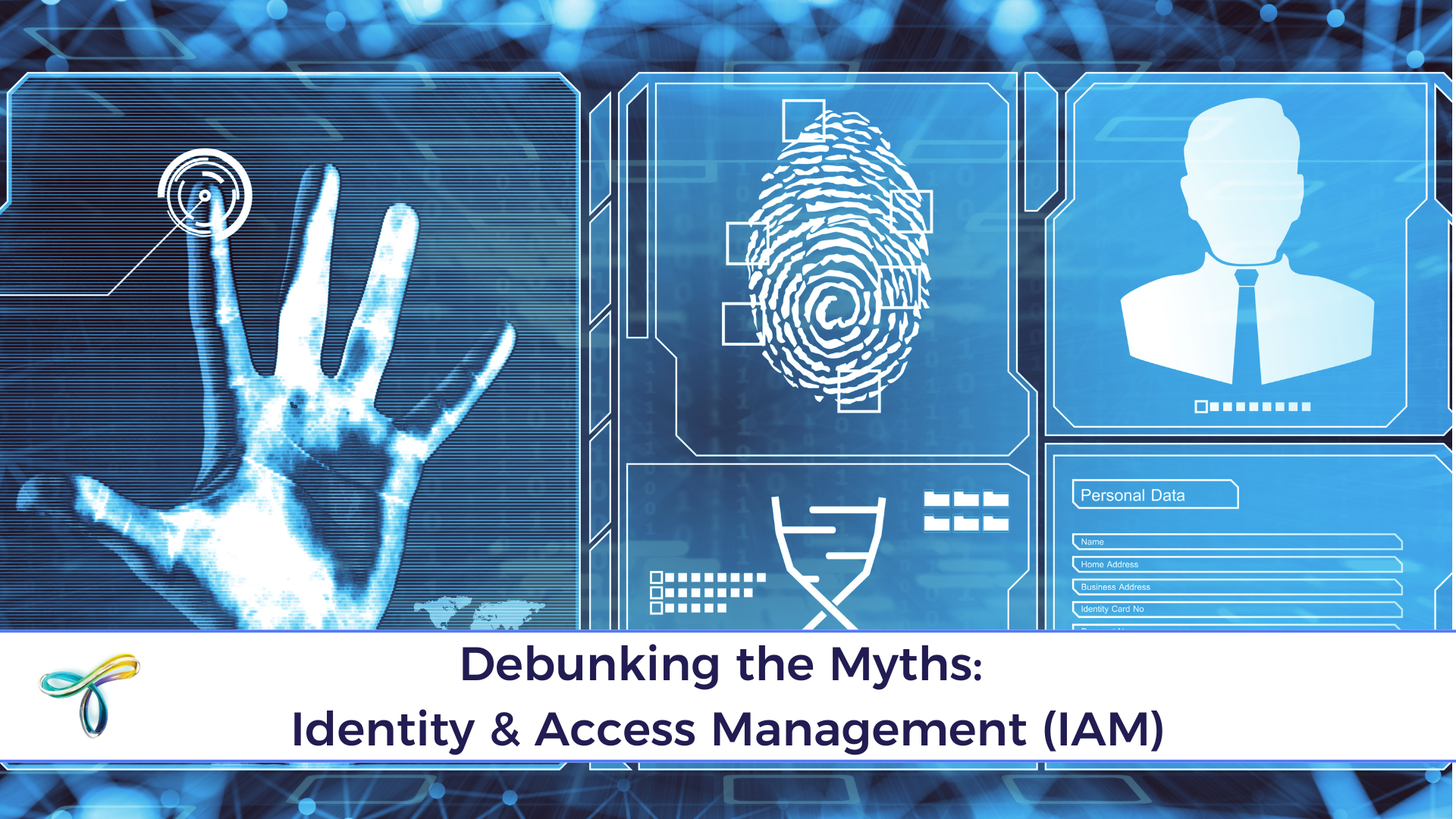
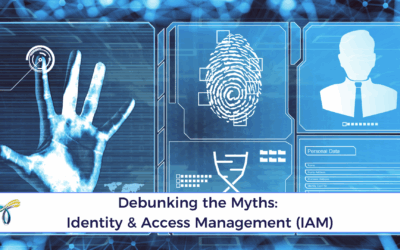
In the world of financial services, trust is everything. Customers entrust banks, investment firms, and payment platforms with their most sensitive data, from personal identification details to transaction histories. However, as financial services embrace digital transformation, the stakes for data security have never been higher. Cyber threats targeting this industry are increasingly sophisticated, and compliance with evolving regulations adds another layer of complexity. In this article, we explore the unique data security challenges in financial services, best practices to protect customer information, and how advanced technologies are fortifying the industry’s digital defences.
Why Data Security Matters in Financial Services
Financial data is among the most targeted by cybercriminals due to its high value. A single breach can compromise not only customers’ personal and financial information but also the reputation and trustworthiness of the institution. The consequences can be dire:
- Identity Theft: Compromised customer data can lead to fraudulent activities, causing financial and emotional distress for victims.
- Reputational Damage: A data breach can erode customer confidence and lead to significant financial losses for the institution.
- Regulatory Penalties: Non-compliance with data protection laws, such as GDPR, CCPA, or PSD2, can result in severe fines and legal repercussions.
The financial sector is also a prime target for ransomware attacks, phishing schemes, and insider threats, making robust data security measures essential for operational resilience and customer trust.
Key Data Security Challenges in Financial Services
The financial services industry faces a unique set of challenges:
- High Volume of Transactions: Millions of transactions occur daily, creating vast amounts of sensitive data that must be protected at all times.
- Third-Party Risks: Financial institutions often rely on third-party vendors and payment processors, which can introduce vulnerabilities into their systems.
- Legacy Systems: Many institutions still operate on legacy IT systems, which lack modern security features and are difficult to update.
- Insider Threats: Employees with access to sensitive data can pose risks, whether through negligence or malicious intent.
- Complex Regulatory Landscape: Adhering to multiple data protection laws across different jurisdictions requires significant resources and expertise.
Best Practices
To protect sensitive financial data, institutions must implement comprehensive security strategies. Here are some best practices:

- Encrypt Data: Use strong encryption protocols to protect data at rest and in transit, ensuring that even if intercepted, the data remains unreadable.
- Adopt Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Require multiple verification steps to access sensitive systems and accounts, reducing the risk of unauthorised access.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Perform periodic assessments of IT systems to identify and address vulnerabilities proactively.
- Monitor Transactions in Real-Time: Deploy AI-driven tools to detect suspicious activity, such as unusual transaction patterns or login attempts.
- Implement Role-Based Access Controls: Restrict data access based on job roles to minimise exposure to sensitive information.
- Train Employees: Educate staff on recognising phishing attempts, secure data handling practices, and regulatory compliance requirements.
Leveraging Technology for Data Security
Advanced technologies are helping financial institutions bolster their defences against cyber threats:
- AI and Machine Learning: AI systems analyse transaction data in real-time to identify anomalies, flagging potential fraud before it escalates.
- Blockchain for Secure Transactions: Blockchain ensures tamper-proof transaction records, enhancing security and transparency in payment systems.
- Cloud Security Solutions: Secure cloud platforms provide scalable storage and robust encryption, supporting secure digital banking experiences.
- Behavioural Biometrics: These systems monitor user behaviour, such as typing patterns and navigation habits, to detect unauthorised access attempts.
Future Trends in Data Security for Financial Services
As cyber threats evolve, financial institutions will continue to innovate in their approach to data security. Key trends include:
- Zero-Trust Architecture: Institutions will adopt zero-trust frameworks that require continuous verification of users and devices accessing data.
- Quantum-Resistant Encryption: With the rise of quantum computing, financial institutions will implement encryption methods designed to withstand quantum decryption.
- Collaborative Cybersecurity: Banks and regulators will work more closely to develop industry-wide standards and share threat intelligence.
- Enhanced Customer Education: Financial institutions will invest in educating customers about secure digital banking practices, empowering them to safeguard their own data.
Protecting Trust in Financial Services
Data security in financial services is about more than compliance—it’s about preserving the trust that underpins the industry. By adopting advanced technologies, implementing rigorous security measures, and fostering a culture of awareness, financial institutions can protect sensitive data and ensure seamless, secure transactions. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, staying ahead of the curve is essential to maintaining customer confidence and ensuring the resilience of the financial ecosystem.