This article explores the Top IAM Features that can help your company overcome security and compliance requirements.
Do you have the right mechanisms to protect your Company’s sensitive data while granting your employees the right access to it at the right time?
Are you struggling to maintain good end-user experience while keeping your data secured?
Did you know you could achieve both while boosting your business performance?
In the last years, businesses both big and small have integrated technology into every service they offer to their clients. With cybercrime growing exponentially, it has become more and more important to secure all assets while ensuring they deliver the best to their customers. Identity and Access Management (IAM) is paramount to protecting sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands, and at the same time guaranteeing everything runs smoothly, thus enhancing the end-user experience.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) encompasses verifying a user’s identity and their corresponding access level to the system. A single digital identity is established for each individual user. Thus, maintenance, modification, and monitoring of the user’s access is simplified. This allows tracking of all user activities, and enforcing security at the same time.
These are the top IAM Features for seamless and secure company operations:
1. Centralised, shared access for enhanced security
IAM allows the creation of separate usernames and passwords for individual users or resources. It can also delegate access to each of them to shared company assets. You can grant certain individuals access to specific service APIs and resources or define specific conditions in which access is granted.
Centralization allows for central reporting as well, securing all business assets.
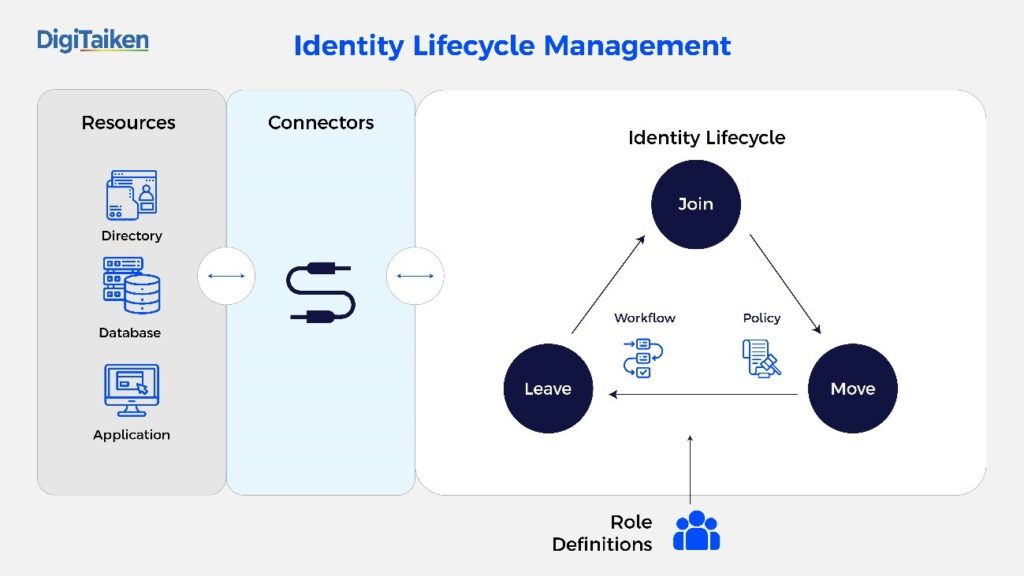
2. Automated User Lifecycles management (LCM)
IAM centralizes and automates Identity Lifecycle Management. This minimizes delays when providing new users with the required tools or denying access to old users. The HR systems provide the source of data that will drive the Joiner, Mover, and Leaver (JML) processes to control the lifecycle of an Identity. This can help ease up the processes of sign-up, sign-in, and user management for users of all kinds, be they application owners, end-users, or system administrators. It simplifies access provisioning and management, developing automated workflows for scenarios such as recruiting or role conversion, thereby promoting user satisfaction and leading to savings in time and a reduction in errors significantly.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication
MFA provides an extra layer of security, in which users provide their username and password plus a one-time, randomly generated OTP from their phone. Adaptive Multi-Factor Authentication is also being adopted, providing flexibility in all environments and enforcing security in an adaptive and risk-based approach.
4. Identity Federation
If a user is already authenticated through another account, such as Facebook or Google, IAM can be made to trust that authentication and allow access based on it.
5. Adherence to Regulatory compliance
All the information regarding Identity and Access Management is provided within a single pane of glass. Its frameworks facilitate policy enforcement regarding user authentication, authorization, and privilege acquisition.
6. Password policy
The most common cause for data breaches is stolen, poor, or default passwords. IAM reinforces the credentials by implementing the best tools to manage them, allowing them to reset or rotate passwords remotely. You can also set rules on passwords, such as how many attempts a user may take before denying access.
One major feature is the Single Sign-On (SSO) capability which, alongside Identity Federation, allows a user to maintain just one password for both on-premises and cloud environment work.
7. Early tracking of harmful activities
With advanced technologies like AI, ML, and risk-based authentication, IAM systems offer identification of spiteful activities and evade them thereby preventing the organization from suffering financial loss. Whenever anomalous behaviour is detected, the session is automatically terminated to avoid breaches.
8. Attribute-based access control (ABAC)
ABAC is an authorization strategy that allows you to create fine-grained permissions based on user attributes. These attributes can be for example department or job role, so that employees are provided access to only those resources they are entitled to. ABAC ensures privileges are not elevated without permission and subsequently restrains the destructions caused by malignant insiders.
In a nutshell, IAM is the go-to strategy to manage and secure the identities of all users and help organizations adhere to regulatory compliances. Defining a modern digital identity and access management (IAM) capability is central to securely operating and conducting business in a threat-increasing environment. IAM helps organizations address the challenges associated with balancing access, compliance, operations, and costs while enhancing security, productivity, and efficiency.
If you need help understanding any of the above points related to Top IAM Features or need more in-depth information on your own IAM Solution implementation, please get in touch with us at sales@digitaiken.com





